Income Needed to Get a Mortgage in Canada

Table of contents
Whether or not you can afford a home depends on many factors. In this blog, we’re on a mission to show you how much mortgage a typical person can afford. We’ll also show you some common calculations needed to understand your home affordability.
Key Highlights
- An income between 3 to 3.5 times your mortgage amount is needed to purchase the average-priced home in Canada with a 20% downpayment.
- The gross annual income of a household needed to purchase an average-priced home is lowest in Newfoundland and highest in Vancouver.
- Your stress-tested mortgage rate, amortization, municipal property tax and downpayment will directly impact the gross income you’ll need to earn to qualify for your mortgage.
How to Calculate Your Mortgage Affordability
Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratios Impact Your Qualifying Rate
Many different factors impact your home affordability, such as the borrower’s credit, the property which is being used as collateral, the borrower’s income capacity to service the debt, the borrower’s capital in the form of savings/investments and downpayment, and most importantly, the conditions. Conditions such as the purpose of the loan and the loan-to-value (LTV) ratio.
Capacity to Service a Mortgage Payment
The most important factor in the qualification process is capacity. What does that mean, exactly? It means that the borrower can make their mortgage payments. It is not enough just to pay the mortgage payment. The lender will stress-test that payment at a higher interest rate. This test also means determining if you can afford the taxes, monthly heating costs and half of the condo fees (if applicable). Secondly, you should be able to carry these payments alongside other outside debts such as car, credit card or student loan payments.
Debt Service Ratios Impact Your Qualifying Mortgage Amount
Capacity is tested with 2 debt-service ratios: Gross Debt Service (GDS) and Total Debt Service (TDS). GDS and TDS are also known as debt-to-income ratios. As the names suggest, GDS calculates the household debt carrying capacity against an applicant’s qualified income, and TDS calculates the total debt carrying capacity against the same income. On joint applications, ratios for qualifying are combined debt payments and incomes in the case of multiple borrowers.
Learn More
GDS Ratio= (Mortgage Payment + Property Taxes + Condo Fees/2 + Hydro) / Income
TDS Ratio = (All debts in GDS calculation + all other debts) / Income
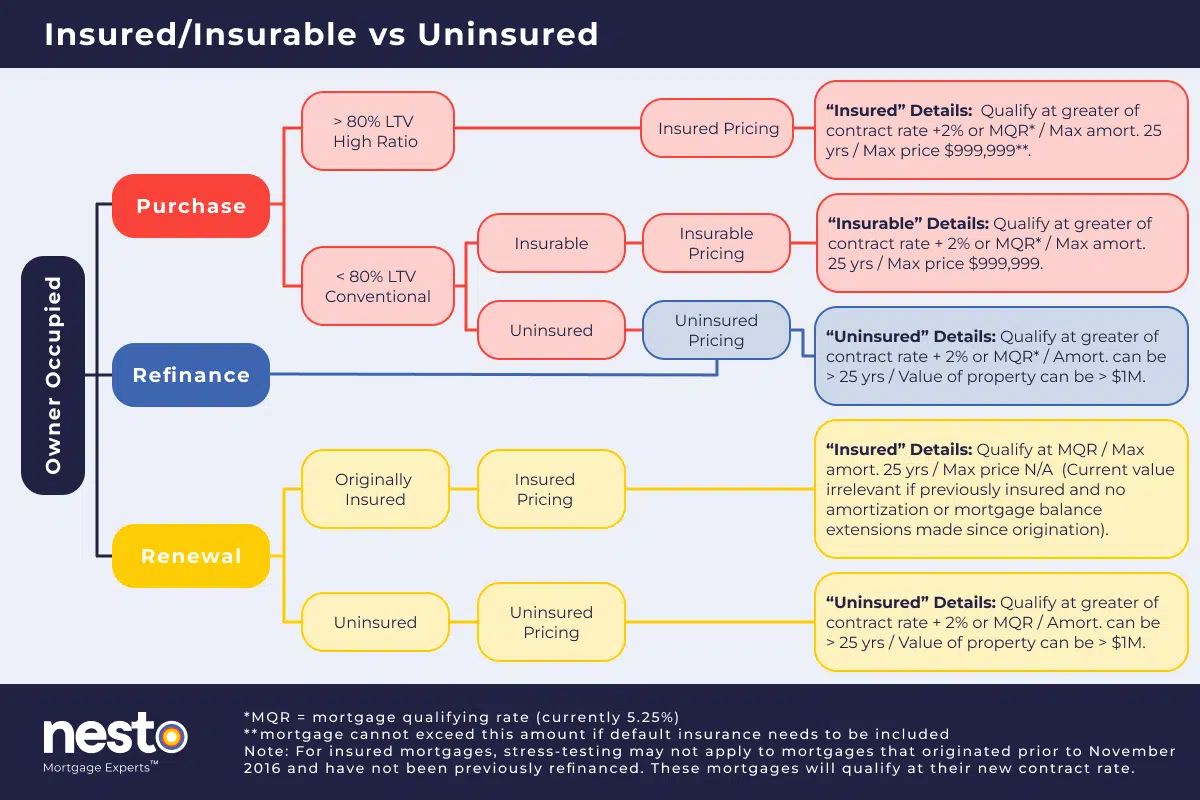
Typically, insured or insurable transactions, where the purchase price or assessed value is under $1 million and the mortgage amortization is limited to 25 years, will lend up to 39% on GDS and 44% on TDS. Some lenders will use different ratios due to their risk appetites.
Uninsured transactions are classified as purchases or renewals where a property is valued at more than $1M, the amortization will be over 25 years, or the transaction is a refinance – where equity is taken out or time is being extended.
In the case of uninsured transactions, lenders will have risk assessment criteria to apply for elevated debt service ratios. In these cases, lenders will consider the client’s unique financial situation. Most lenders will have lower debt service ratios when the risk is higher, such as for a refinance or an uninsured transaction, or if one of the borrowers has a lower FICO score than their required minimum.
|
Transaction Type & Limitation |
Maximum Allowable GDS |
Maximum Allowable TDS |
|---|---|---|
| Credit Score (FICO) 650 and 680 (on the lower-scoring applicant, insured only) | 32 | 40 |
| Uninsured Transaction – purchase of property valued at $1M + or a refinance where a mortgage can be amortized up to 30yrs | 35 | 42 |
| Insured / Insurable Transaction – purchase or renewal of property valued less than $1M where a mortgage is limited to 25 years of amortization. | 39 | 44 |
For our primary example, we will use an annual income of $100K, which would be the joint income of 2 borrowers servicing the mortgage together if they made $50K each annually.
For our example, we will use the widely accepted and used debt service ratios of 39% GDS and 44% TDS. We will consider taxes at 1% of property value to simplify property tax rates across Canada, ranging from 0.27% in Vancouver to 3.27% in Manitoba. However, as two of the biggest markets, Greater Vancouver and Greater Toronto, are well below the national average, we’ll use 1% wherever an average is unavailable. We will simplify the heating (utility) cost for all properties at $100/month.
We will also assume that the client does not have any outside debts or condo fees, though the easiest way to survey how these items affect your purchasing power is to look at what fraction of your monthly mortgage payment they affect. As you only have 5% to work with on a difference between 39% on GDSR and 44% on TDSR, it is best to think of this as an annual amount. So, if the borrower earns $100K, any outside debts cannot exceed an annual payment of $5,000 or a monthly payment of $416.
GDS = Income $100,000 x 0.39 GDS / 12 = $3,250 monthly
TDS = Income $100,000 x 0.44 TDS / 12 = $3,666 monthly
That means that a person or family earning a combined income of $100K will be able to service monthly mortgage payments, property taxes, and heating (plus ½ condo fees) up to a maximum of $3,250. They can carry up to $416 monthly in outside debts, such as car loans and student loans, or up to 3% of the balance of all revolving debts ($416/0.03), meaning up to a $13,867 balance on your credit card or lines of credit combined.
Passing the Mortgage Stress Test
You’ll have to pass the stress test to qualify for the mortgage. This will entail proving that you can afford payments at a qualifying interest rate, typically higher than the actual rate in your mortgage contract.
You will need to pass a stress test to qualify for a mortgage, regardless of whether you need mortgage default insurance. Federally regulated lenders must be able to show that you can service your loan at the higher of the contracted interest rate plus 2%, or 5.25%.
Mortgage Default Insurance
An insured mortgage is where your downpayment is less than 20%, cannot exceed 25 years amortization, and the purchase price is less than $1 million. You will need to purchase default (high-ratio) insurance whenever you put less than 20% down as a downpayment. Although this insurance can be added to your mortgage, the taxes (PST) on purchasing this insurance cannot.
Learn More
Upon closing, your solicitor will collect and remit the taxes (PST) on behalf of the high-ratio insurer (CMHC, Sagen, or Canada Guaranty). Once high-ratio default insurance is purchased from one of the 3 default insurers, the lender’s risk is reduced, as the insurance will protect them in case of default.
All things being equal, the lowest rate, in this case, will be an insured purchase or renewal. An insured renewal is one where the borrower purchased default insurance with the home. The second lowest rates apply to an insurable purchase where the borrower puts down 35% or more of the purchase price in a downpayment. Similarly, this also applies to renewals where the property has 35% or more equity at the time the mortgage is renewed.
An insurable transaction means that the lender arranged insurance on the backend to protect themselves from the borrower defaulting – this automatically comes with better rates even though the lender pays for the (much lower) insurance premium.
| Loan-to-Value | Premium |
|---|---|
| 80.01% to 85% | 2.80% |
| 85.01% to 90% | 3.10% |
| 90.01% to 95% | 4.00% |
Housing Affordability by Province
Month-over-Month Change
Compared to last month in Canada’s provinces, the average home price change and the income required to qualify for a mortgage on that average-priced home.
Calculations are based on a mortgage with a 25-year amortization, a 20% downpayment, provincially averaged property tax rate and includes $100 for monthly heating costs. Home prices are sourced from the most recent CREA report.
Housing Affordability by Province
Year-over-Year Change
Compared to last year in Canada’s provinces, the average home price change and the income required to qualify for a mortgage on that average-priced home.
Calculations are based on a mortgage with a 25-year amortization, a 20% downpayment, provincially averaged property tax rate and includes $100 for monthly heating costs. Home prices are sourced from the most recent CREA report
Housing Affordability by City
Month-over-Month Change
Compared to last month in some of Canada’s cities, the average home price change and the income required to qualify for a mortgage on that average-priced home.
Calculations are based on a mortgage with a 25-year amortization, a 20% downpayment, provincially averaged property tax rate and includes $100 for monthly heating costs. Home prices are sourced from the most recent CREA report report.
Housing Affordability by City
Year-over-Year Change
Compared to last year in some of Canada’s cities, the average home price change and the income required to qualify for a mortgage on that average-priced home.
Calculations are based on a mortgage with a 25-year amortization, a 20% downpayment, provincially averaged property tax rate and includes $100 for monthly heating costs. Home prices are sourced from the most recent CREA report
Income Needed to Buy an Average-Priced Home in Canada
As nesto has some of the best rates for insured or insurable purchases anywhere, we use our fixed and variable rates to illustrate the income needed for typical home prices across Canada.
For this exercise, we will use a 1% property tax rate, which is the average that applies to areas where 80% of the population lives in Canada. We will assume a minimum required downpayment of 10% on the purchase price. However, for insured purchases, you need a minimum downpayment of at least 5% on the first $500,000 and 10% on the purchase price above $500,000.
Income Needed to Buy an Average-Price Home in Canada on an Insured Fixed Rate
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization:
Income Needed to Buy an Average-Price Home in Canada on an Uninsured Fixed Rate
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
Income Needed to Buy an Average-Priced Home Across Quebec
Compare the income you need to purchase the average-priced home in Québec or some of its large cities and regions, including Montréal and Québec City.
Income Needed to Buy an Average-Priced Home Across Ontario
Compare the income you need to purchase the average-priced home in Ontario or some of its large cities, including Toronto and Mississauga.
Income Needed to Buy an Average-Priced Home Across Alberta
Compare the income you need to purchase the average-priced home in Alberta or some of its large cities, including Calgary and Edmonton.
Income Needed to Buy an Average-Priced Home Across British Columbia
Compare the income you need to purchase the average-priced home in Alberta or some of its large cities, including Vancouver and Victoria.
Income Needed to Buy an Average-Priced Home Across the Prairie Provinces
Compare the income you need to purchase the average-priced home in the Prarie provinces or some of their large cities, including Saskatoon and Winnipeg.
Income Needed to Buy an Average-Priced Home Across the Maritime Provinces
Compare the income you need to purchase the average-priced home in the Prarie provinces or some of their large cities, including Halifax and Moncton.
What Does the Average Income Buy You Across Canada
Income Needed to Buy an Average-Priced Home in Different Provinces
There is no simple or blanket answer to the qualifying income amount across Canada, as each municipality in every province has its own municipal property tax rate, which directly affects the income needed to qualify.
Income Needed to Buy an Average-Priced Home in Canada’s Large Cities
There is no simple or blanket answer to the qualifying income amount across Canada, as each municipality’s own property tax rate directly affects the income needed to qualify.
We’re curious…
Income Needed for Different Types of Mortgages
Income Needed to Qualify for Mortgage on Our Insured Fixed Rate
Calculations are based on a mortgage with a 25-year amortization, a 20% downpayment, provincially averaged property tax rate and includes $100 for monthly heating costs. Home prices are sourced from the most recent CREA report.
Income Needed to Qualify for Mortgage on Our Insured Variable Rate
Calculations are based on a mortgage with a 25-year amortization, a 20% downpayment, provincially averaged property tax rate and includes $100 for monthly heating costs. Home prices are sourced from the most recent CREA report.
Income Needed to Qualify for Mortgage on Our Uninsured Fixed Rate
Calculations are based on a mortgage with a 30-year amortization, a 20% downpayment, provincially averaged property tax rate and includes $100 for monthly heating costs. Home prices are sourced from the most recent CREA report.
Income Needed to Qualify for Mortgage on Our Uninsured Variable Rate
Calculations are based on a mortgage with a 25-year amortization, a 20% downpayment, provincially averaged property tax rate and includes $100 for monthly heating costs. Home prices are sourced from the most recent CREA report.
Income Needed to Qualify for Common Mortgage Balances
In this section, we will qualify some common mortgage amounts that borrowers show interest in. Typically, $100K, $200K, $300K, $400K, $500K, $600K, $700K, $800K, $900K and $1 million mortgages are quite popular in Canada. To simplify the qualifying criteria, we have used 30yrs amortizations with a 20% Downpayment, thus revealing the carrying costs of a typical balance without any mortgage default insurance premiums added to those balances.
It is important to highlight that lenders will use lower debt service ratios when mortgages are not default-insured; therefore, instead of including 39% of the borrower’s gross income, they will typically use 35%. Also, it is important to mention that if your credit score is below 680, lenders will prefer that your loan is default insured with less than 20% downpayment to avoid additional risk to themselves – and qualify you on a GDS ratio of 32% (not used in any of our calculations here).
Income Needed for a $100,000 Mortgage in Canada
How much income do you need to qualify for a $100,000 mortgage in Canada?
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization:
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
Income Needed for a $200,000 Mortgage in Canada
How much income do you need to qualify for a $200,000 mortgage in Canada?
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization:
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
Income Needed for a $300,000 Mortgage in Canada
How much income do you need to qualify for a $300,000 mortgage in Canada?
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization:
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
Income Needed for a $400,000 Mortgage in Canada
How much income do you need to qualify for a $400,000 mortgage in Canada?
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization:
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
Income Needed for a $500,000 Mortgage in Canada
How much income do you need to qualify for a $500,000 mortgage in Canada?
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization:
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
Income Needed for a $600,000 Mortgage in Canada
How much income do you need to qualify for a $600,000 mortgage in Canada?
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization:
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
Income Needed for a $700,000 Mortgage in Canada
How much income do you need to qualify for a $700,000 mortgage in Canada?
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization:
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
Income Needed for a $800,000 Mortgage in Canada
How much income do you need to qualify for an $800,000 mortgage in Canada?
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization:
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
Income Needed for a $900,000 Mortgage in Canada
How much income do you need to qualify for a $900,000 mortgage in Canada?
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization does not apply on properties valued at $1 million or more:
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
Income Needed for a $1,000,000 Mortgage in Canada
Properties valued at $1 million or more cannot be purchased in Canada with mortgage default insurance. Purchasing a property of $1 million or more in valuation requires a downpayment of 20% or greater, calculated on the lower of the appraised value or purchase price. When the lender or appraiser assesses the subject property value as $1 million or more, the mortgage rate will always be the higher uninsured rate. Uninsured rates are not impacted by the amortization, allowing up to 30 years with prime lending.
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization does not apply on properties valued at $1 million or more:
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
Frequently Asked Questions
What salary do I need to buy a house in Canada?
You can buy a house in Canada on any salary. The salary required to qualify for a mortgage will depend on the stress-tested mortgage payment, property taxes and heating costs. We recommend you have an in-depth conversation with your realtor and mortgage expert before purchasing. Or simply just give us a call at nesto!
How many times my salary can I borrow for a mortgage in Canada?
You will qualify for about 3.5 times your income if you put less than 20% downpayment; conversely, you’ll qualify for approximately 3 times your income if you have saved more than 20% towards your downpayment. These ratios don’t apply to all situations, as municipal tax rates differ quite a bit between municipalities and provinces. Typically, property tax rates are lower in areas with higher population densities. Conversely, these areas have higher property values as they are more sought after.
Why choose a 25-year versus a 30-year amortization?
Choosing an amortization of 25 years versus 30 years can save you a lot of money on your cost of borrowing, that is, the interest charged over the life of the mortgage. Suppose your property value is less than $1 million. In that case, it may be worthwhile to discuss insured pricing options with your mortgage expert as this might save you not only on interest costs (rates can be quite a lot lower on insured mortgages) but also make it easier to qualify since you can use up to 39% of your income to carry your mortgage.
What income is needed for each $100K mortgage balance?
An annual income between $27,625 and $34,100 is needed to qualify for a $100,000 mortgage balance. The range is provided based on whether your selected mortgage rate is fixed or variable, stress testing on the current lowest rates at nesto and applying a range of gross debt service ratios depending on factors such as your downpayment and credit score. As of April 26, 2024, our lowest 5-year fixed mortgage rate is
What other costs should I consider when purchasing a home in Canada?
There are various other costs to consider when purchasing your home. You should set aside 1.5% to 2.5% of the purchase price for closing costs, land transfer taxes, inspections, appraisals, taxes on default insurance, and other costs not mentioned here. Your mortgage and real estate professionals can highlight any costs specific to your purchase.
How nesto works
At nesto, all of our commission-free mortgage experts hold concurrent professional designations from one or more provinces. Our clients will receive the best advice and care when they speak with specialists that exceed the industry status quo.
Unlike the industry norm, our agents are not commissioned but salaried employees. This means you’ll get free, unbiased advice on the most suitable mortgage solution for your unique needs. Our advisors are measured on the satisfaction and quality of advice they provide to their clients.
nesto is working hard to change how the mortgage industry functions. We start with honest and transparent advice, followed by our best rates upfront. We can offer you these low rates using the fintech industry’s best-in-class and safest technology to provide a 100% digital online experience and process to reduce overhead costs.
By working remotely across Canada, all our mortgage experts and staff spend less time commuting to work and more time with their friends and family. This makes for more dedicated employees and contributes to our success with happy and satisfied clients.
nesto is on a mission to offer a positive, empowering and transparent property financing experience, simplified from start to finish.
Reach out to our licensed and knowledgeable mortgage experts to find your best mortgage rate in Canada.
EXPLANATIONS
Rates
Values
Rents
Criteria
Experts
Titles
Interest Rates
Qualified using nesto’s fixed 5-year insured and uninsured rates as advertised on our website. For today, Friday, April 26, 2024, our example calculations are qualified on our lowest rates, which may or may not apply to your unique financing situation or long-term goals. Insured fixed-rate mortgages will be qualified at
We appreciate your patience and understanding and encourage you to email us at website@nesto.ca with information that needs correction alongside your sources.
Property Values
Home values collected from CREA or QPAREB are those presented as the composite benchmark or average prices for each city/province/region unless specified. They may be interchangeably called average home prices, though an average price may not be available for many regions outside Quebec.
Rents
Our monthly or year-over-year rental averages are sourced from Urbanation’s monthly Rentals.ca National Rental Report.
Mortgage Qualifying Criteria
Insured qualifying criteria are limited to a 39% gross debt service (GDS) ratio and up to 25 years of amortization. For insured mortgage transaction calculations, we have used a 20% downpayment, unless otherwise indicated, in our examples and excluded any mortgage default insurance (CMHC) premium. Uninsured qualifying criteria are limited to a 35% gross debt service (GDS) ratio and up to 30 years of amortization. Our examples use a 20% downpayment for uninsured mortgage transaction calculations. Unless otherwise indicated, a $100 monthly heating cost is attributed to the total monthly stress-tested payment. Municipal tax rates are the most recently shown on the applicable municipality’s website (1% used as default when unavailable or for a region with an unspecified mill rate). Mortgage default insurance is not permitted on purchases that have valuations of $1 million or more, amortizations exceeding 25 years, or on refinance transactions.
nesto Mortgage Experts
Titles such as mortgage broker, mortgage agent, submortgage broker, mortgage salesperson, or principal broker are provincially regulated licensing terms with educational requirements specific to each province. Albeit, commonly, they may all be referred to as mortgage brokers. In Ontario, where mortgage agent is used as a designation, mortgage brokers or principal brokers have additional responsibility for compliance and training mortgage agents.
Licensed mortgage professionals often use the industry norm of “mortgage broker,” “broker,” or “advisor” to refer to themselves. However, disclosure requirements for licensed mortgage professionals’ titles vary across each province in Canada. These disclosures require mortgage brokers to adhere to specific rules when using titles to represent their qualifications and expertise. The provinces have regulations and guidelines that govern the use of titles by mortgage brokers. These regulations aim to ensure transparency and protect consumers in the mortgage industry.
Regulatory Titles
In Ontario (FSRA), Mortgage Brokers and Agents both serve as the middle person between borrowers and lenders, helping clients find the most suitable mortgage options for their financing situation. A Mortgage Agent works under the supervision of a Mortgage Broker and assists in the mortgage application process. A Mortgage Broker may also be responsible for compliance requirements for their brokerage or a team.
The provinces of Quebec (AMF) and Newfoundland (Digital & Government Service NL) both exclusively utilize the designation of Mortgage Broker as a licensing designation.
British Columbia (BCFSA) has two distinct roles within the mortgage industry: the Submortgage Broker and the Mortgage Broker. These positions have specific responsibilities and functions that contribute to the overall process of securing mortgages for clients. The Submortgage Broker works under the supervision of a licensed Mortgage Broker and assists in various tasks, such as gathering client information, completing paperwork, and liaising with lenders. The Mortgage Broker oversees the entire mortgage application process, including assessing client needs, finding suitable mortgage options, negotiating terms, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
In Alberta (RECA) and New Brunswick (FCNB), the distinction between a Mortgage Associate and a Mortgage Broker lies in their roles and responsibilities within the mortgage industry. A Mortgage Associate typically works under the supervision of a Mortgage Broker and assists in the mortgage application process gathering necessary documentation, and providing support to clients. A Mortgage Broker is licensed to independently negotiate and arrange mortgage loans on behalf of clients, offering a more comprehensive range of mortgage options and expertise in the field.
In Saskatchewan (FCAA) and Nova Scotia (Government of Nova Scotia, Business Licensing), there are distinct roles for both Associate Mortgage Brokers and Mortgage Brokers. The critical difference lies in their level of experience and licensing requirements. Associate Mortgage Brokers work under the supervision of a licensed Mortgage Broker and are in the early stages of their career. They may assist with gathering client information and preparing mortgage applications. Mortgage Brokers have obtained the necessary qualifications and licences to operate independently and provide mortgage services directly to clients. They have the authority to negotiate mortgage terms, advise clients, and facilitate the mortgage process from start to finish.
In Manitoba (MSC), a Salesperson is primarily responsible for promoting and selling products or services, while an Authorised Official holds the authority to make legally binding decisions on behalf of the organization. These roles have different levels of authority and expertise, with the Salesperson focusing on sales and the Authorised Official having broader decision-making powers and acting as the liaison between the brokerage and the regulator.
For a complete list of licensing terms in Canada, please see the Mortgage Broker Regulators’ Council of Canada (MBRCC) published list.
Ready to get started?
In just a few clicks, you can see our current rates. Then apply for your mortgage online in minutes!